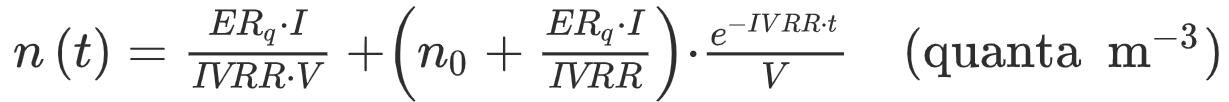Covid-19 Infection Risk Calculator
Introduction
A Powerful Calculator for Everyone
Our calculator features great extensibility while maintaining the ease of use. Estimations are made based on solid researches, normal users can easily use default settings to get decent estimations, while advanced users can import their custom rooms and modify assumptions based on the situation in their own regions. We also provide an interactive visualization for convenient comparison between cases.
Methods
To calculate the risk of airborne infection in a given room the emission rate of quanta is needed. A quantum is defined as the viral load i.e. the dose of contaminated airborne droplet nuclei required to cause infection in 63% of persons. The emission rate of quanta is calculated with the following formula from Morawska et al. 2020 :
Where Ni is the droplet concentration by diameter. These droplet concentrations were taken from Morawska et al. 2009.
Cv corresponds to the viral load in the sputum (i.e. infectious mucus) of the infected person. The viral load in the sputum of an infected person varies and is dependent on the stage of infection so for this estimator we will choose a large viral load of 1e9 RNA copies per milliliter to simulate the worst case scenario for infection spread [based on Walsh et al. 2020 ].
IR (Inhalation Rate) the product of breathing rate and tidal volume, expressed in cubic meters per hour. IR is dependent on the activity of the infected subject. We chose IR values from Adams 1993 .
To calculate the concentration of quanta over time we are using the following equation based on Gammaitoni and Nucci's 1997 paper:
IVRR (hr−1) represents the infectious virus removal rate in the room. The IVRR is the sum of three parameters: the air change per hour (ACH) via ventilation, the particle deposition on surfaces via gravitational settling which is 0.63 according to Doremalen et al. 2020, and the viral inactivation rate which is 0.24 per hour according to Chatoutsidou and Lazaridis, 2019.
n0 represents the initial number of quanta in the space, we presume there is no initial quanta, which means n0 = 0.
I is the number of infected people.
V is the volume of the indoor environment considered.
After collecting all information above, we can calculate the estimated infection risk R using the formula:
Resulting Application
Here is the link to our application: https://hinanawits.github.io/DSC-180B-Presentation-Website/
This is what the application looks like without any inputs:
After adding parameters, this is what the final result will end up looking like:
We are using building data that we scraped from the University of California, San Diego facilities website, but if you have your own building data you can enter your own csv and calculate how safe your buildings are
There is a set layout you need your csv to be in for the calculator to properly read your data
Questions?
Feel free to contact me at nichkho2@gmail.com or if check out our motivations and tutorial video on this project at: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PvhIIPIV9rA